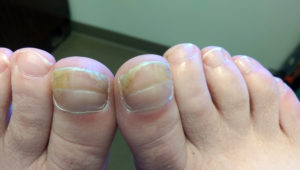
 Fungal infection of the toenails and fingernails is referred to as onychomycosis. It appears as white or yellowed nails that may be thickened and brittle. One or more nails may be involved, and different parts of a nail may be affected.
Fungal infection of the toenails and fingernails is referred to as onychomycosis. It appears as white or yellowed nails that may be thickened and brittle. One or more nails may be involved, and different parts of a nail may be affected.
Toenails are the most vulnerable to fungal infection because shoes and socks trap moisture that promotes the growth of fungi.
If left untreated, fungal infections can lead to permanent nail damage.
Fungal infections of the nails are difficult to treat, and recurrence is common. Most antifungal medications applied to the directly onto the nail (topical) are not every effective because they cannot penetrate the hard nail in sufficient concentration to kill the fungi. There are, however, some formulations specifically designed to penetrate the nail.
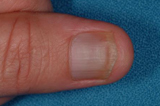
 If the fungal infections have already reached the nail bed (the place where the nail starts growing), oral medications may be prescribed. These medications reach the nail bed through the blood.
If the fungal infections have already reached the nail bed (the place where the nail starts growing), oral medications may be prescribed. These medications reach the nail bed through the blood.
If a nail is badly damaged, nail removal may be recommended.
Follow these steps to prevent fungal nail infections:
- Practice good hygiene and keep hands and feet clean.
- Keep your skin dry, especially between the toes.
- Wear shower sandals in damp public places, such as swimming pools and locker rooms.
- Keep your nails trimmed and clean.
- Wear well-ventilated shoes, and change socks regularly, especially after exercise.
- Wear rubber gloves when washing dishes or doing other housework that could overexpose your hands to moisture.
- Sterilize any instruments you use on your nails before and after every use. This includes nail clippers and any instruments used in manicures or pedicures.
- Wash your hands after touching an infected nail.